Resources
当前位置: 首页»
Resources

Cube Elimination(方块消消乐)
Game Introduction
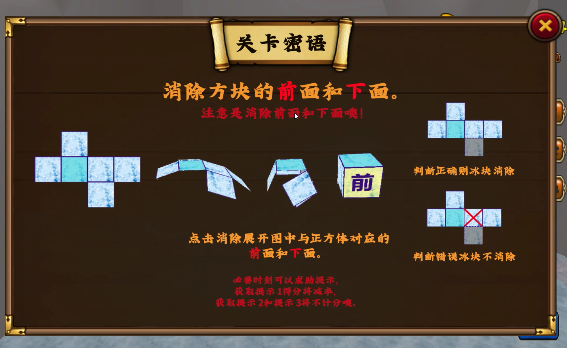
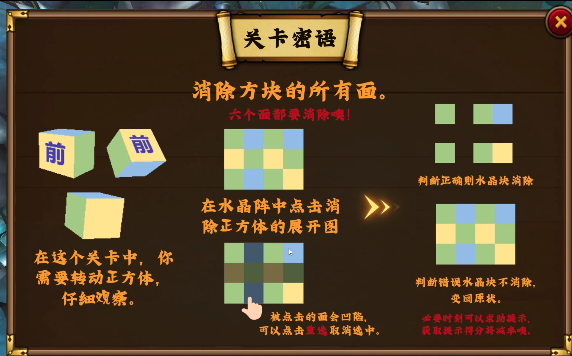
Cube Elimination is the result of a series of educational game research projects based on the learning sciences perspective carried out by the Lab of Learning Sciences, Graduate School of Education, Peking University. Cube Elimination is an elimination educational game designed to enhance students’ math performance and mental folding ability. From the perspective of learning Sciences, Elimination Cube integrates the studies and theories of neuroscience, psychology and pedagogy, matches the Chinese mathematics curriculum standard, and follows students’ cognitive development. It is suitable for the fifth-grade (children aged 10-11) "nets folding and unfolding" learning and classroom teaching. Learners of all ages can use it to develop their mental folding ability as well. Based on neuroscience and psychology studies, we designed the activity, asking students to fold the 2D graphics into 3D graphics, which is the most effective way to promote this content learning. Moreover, the step-by-step task that meets the characteristics of students’ cognitive and thinking development is set up to ensure the scientific of this game. In addition, to match the classroom teaching, we deeply analyzed the content of Chinese mathematics curriculum standard and popular textbooks and organized the content of Cube Elimination in a progressive way: the identification of the opposite side of a cube, the identification of the front and top/bottom sides, and the identification of the cube nets. Based on the related research of pedagogy, the cognitive scaffolding, 2D-3D graphics transformation animation, is designed to help students construct representation and ensure the effectiveness of the game. Based on the theory of educational games, game mechanisms such as story, points, and rewards are designed to enhance the fun of the game. The elimination activities of Elimination Cube include the elimination of the opposite side of a cube, the elimination of the front and top/bottom sides, and the elimination of the cube nets to enhance students’ ability to represent 2D graphics, 3D graphics, and 2D-3D transformation. Fist, the player can register, fill in the basic information, and log in to the game. After entering the level selection interface, there are three maps, including Flame, Glacier and Crystal. In the initial state, the player needs to start from the first level of the Flame to gradually unlock the level and map. In every level, the player needs to find, click and eliminate the opposite side of the cube. If the player selects the correct side, it is eliminated, and the score is increased by one. If the selection is wrong, the side is not eliminated and error feedback is displayed. Players need to eliminate enough sides within a limited number of steps. The level in the Flame is to eliminate the opposite side of the cube. If the player has difficulty, two kinds of hints are provided, one is the 3D cube model, and the other is the dynamic animation of the 2D-3D graphics transformation process. The level in the Glacier is to eliminate the front and top/bottom of the cube. The level in the Crystal is to observe the 3D cube and eliminate the cube nets. After every level, the player will get feedback on the results. Players who get 2 stars and above will be able to continue the next level, otherwise the next level will be locked. Moreover, players who score 3 stars will definitely get the reward. Players who score 2 stars have a one-third chance to get the reward. Players can view the rewards they have at the backpack. After collecting all the rewards of one map, players can unlock the next map, otherwise the map will be locked. The effect of Elimination Cube was studied, and it was found that the educational game can enhance the academic performance and mental folding ability of grade 5 students. The quasi-experiment found that there was a significant difference in the academic performance between the game group and the control group. The academic performance of the game group was higher than that of the control group. Applying the game into the mathematics classroom, the data of 115 students showed that after 40 minutes per day, 3 days of intervention, the average score of mathematics learning increased by 60%, and the average score of mental folding ability increased by 11%.